How does air pollution affect our health?
Breathing in polluted air can be very bad for our health. It can make it difficult to breathe and cause diseases such as respiratory disorders, lung cancer and heart disease. Air pollution is especially dangerous for children living near polluted areas.
Many people die each year from the direct or indirect effects of air pollution.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pollutants that pose the greatest risk to a person’s health are:
- Particles (particulate contaminants), which include suspended solids and liquid droplets
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulphur dioxide
- Ozone
Effects of short-term exposure
Some health effects may show up shortly after a single exposure or repeated exposures to a pollutant. Such immediate effects are usually short-term and treatable. Sometimes the treatment is simply eliminating the person’s exposure to the source of the pollution if it can be identified.
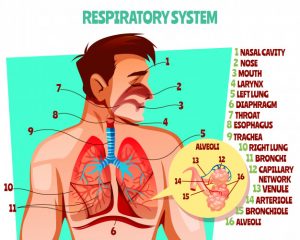
Affect the Respiratory System
Short-term exposure to air pollution, such as ground-level ozone, can affect the respiratory system because the majority of the pollutants enter the body through a person’s airways.

Reduced Lung Function
Short-term exposure to air pollution may lead to reduced lung function.
It may also aggravate asthma in people with this condition.

Affect the Eyes & Skin
Exposure to sulfur dioxide may cause damage to the eyes and respiratory tract, as well as irritating the skin, nose and throat.

Headaches, Dizziness & Fatigue
Exposure to polluted air can make pregnant women more likely to experience preterm delivery.
Effects of Long Term Exposure
Some health effects may show up either years after exposure has occurred or only after long or repeated periods of exposure. These effects can be severely debilitating or fatal. As we mentioned in indoor air quality we live most of our time in buildings so try to improve the indoor air quality in your home even if symptoms are not noticeable.
Lung Cancer
According to the WHO, air pollution causes 29% of all lung cancer cases and deaths.
Particle pollutants are likely to contribute to this figure significantly as their small size allows them to reach the lower respiratory tract.
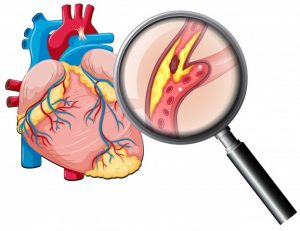
Heart Diseases
Research shows that living in an area with higher levels of air pollution may increase the risk of death from stroke. Air pollution may trigger stroke and heart attacks.
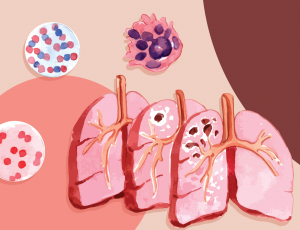
COPD - type of obstructive lung disease
Exposure to particle pollutants may cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). According to the WHO, air pollution causes 43% of COPD cases and deaths worldwide.

Premature Birth
Exposure to polluted air can make pregnant women more likely to experience preterm delivery.